Juvenile Substance Abuse Prevention Program
Posted By admin On 12.09.19- Effective Substance Abuse Prevention Programs
- Community Substance Abuse Prevention Programs
- Center For Substance Abuse Prevention
Elements of Effective Prevention Programs There is a multitude of effective substance abuse prevention interventions that may have different areas of focus and can be implemented in a variety of settings. Interventions can involve the family, school, and community and may provide substance abuse prevention for an. The Juvenile and Adolescent Substance Abuse Prevention Program (JASAP) is a curriculum-based prevention and health promotion program for youth between the ages of 13 to 18 years in.
Evidence-Based Substance Abuse Programs for Juveniles
Juvenile Substance Abuse Treatments are programs that aim to reduce risk factors and promote protective factors related to substance use and abuse. Interventions range in intensity and frequency of services provided including prevention, education, and treatment. In addition, treatment programs for juveniles are consistent with a developmental framework and are inclusive of the multiple systems that the juvenile is part of including school, family, and communities.
Midwestern Prevention Project
Midwestern Prevention Project (MPP) is a community-based program focused on the prevention of adolescent drug abuse. The MPP targets several contexts, beginning in schools and eventually extending into family and community settings. The program aims at helping youth develop awareness of the social pressures to use drugs, as well as the skills to avoid drug use.
Resources
Project Towards No Drug Abuse
Project Towards No Drug Abuse (Project TND) is a prevention program aimed at at-risk high school youth. The program focuses on providing youth with self-control skills, communication skills, resources that help resist drug use, improved decision-making strategies, and the motivation to avoid drug use.
Resources
Guiding Good Choices
Guiding Good Choices (GGC) is a drug-use prevention program targeting the families of adolescents and children in grades 4 through 8 (9 to 14 years old). The goal is to provide these families with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate early adolescence. The program seeks to strengthen and clarify family expectations for behavior, enhance the conditions that promote bonding within the family, and teach skills that allow children to resist drug-use successfully.
Resources
Project ALERT
Project ALERT is a school-based prevention program for middle or junior high school students that focuses on alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana use. It seeks to prevent adolescent non-users from experimenting with these drugs, and to prevent youths who are already experimenting from becoming more regular users or abusers.
Resources:
Intensive Protective Supervision Project
Intensive Protective Supervision Project (IPSP) is a program that aims to remove juvenile offenders from criminal justice institutions and provide them with more proactive and extensive community supervision than they would otherwise receive. Its primary goals are to reduce undisciplined acts, decrease the likelihood of future, serious delinquency, and increase socially acceptable behaviors.
Resources
Orange County Juvenile Substance Abuse Treatment Court
Orange County Juvenile Substance Abuse Treatment Court (JSATC), in its design and operation, resembles other drug courts operating across the country. The program targets first-, second-, third-, and fourth-time juvenile offenders with no history of violent offense who are in need of substance abuse treatment and reside in Orange County, Florida. Individuals can enter the program either on a voluntary basis or by order of a judge. Participation is encouraged by offering diversion from prosecution or reduction of charges upon completion of treatment. While most participants receive outpatient treatment, a few receive inpatient services.
Treatment services concentrate on “breaking” behavioral patterns of addiction, changing irrational thinking patterns into rational thinking patterns, enhancing motivation for treatment, and providing exposure and access to supportive influences, as well as meeting educational and vocational needs and developing life skills.” Outpatient services include individual sessions, group sessions, family meetings, and educational services. The length of stay in the outpatient treatment program ranges from 4 to 8 months, with an average stay of 6 months, depending on the individual’s identified course of care and progress in the program. Participants are required to attend treatment sessions and regular meetings with the case manager, observe a curfew, appear in court for case reviews with a supervising judge, and abide by all local, State, and Federal laws.
Resources
Delaware Juvenile Drug Court Diversion Program
Delaware Juvenile Drug Court Diversion Program helps first-time juvenile misdemeanor drug offenders develop the skills and maturity necessary to prevent further criminal behavior. All juveniles in the program receive case management services from a private agency that provides outpatient drug abuse prevention, intervention, and treatment services to teens. The services the program provides to juveniles include regular urine screenings, court reporting, and accompaniment for monthly court reporting. The program asks that juveniles maintain sobriety, attend all scheduled treatment sessions, and refrain from criminal activity. Due to the treatment nature of the program, noncompliance does not result in termination. However, to graduate from the program, the juvenile must complete all of his or her treatment goals, and be in compliance with the program for a significant period. Graduation results in the dismissal of charges.
Juveniles interact with the nonprofit agency Services to Overcome Drug Abuse Among Teenagers (SODAT) at one of three levels of intensity, but all participants receive SODAT case management services. One group receives case management from SODAT but receives treatment services elsewhere. Another group receives SODAT case management along with educational programs, family counseling, job training, and scholastic intervention. A third group receives SODAT case management with treatment groups, individual counseling, and family counseling.
Resources
Maine Juvenile Drug Treatment Court
Maine Juvenile Drug Treatment Court is based out of Maine, one of the few States to successfully implement a statewide system of juvenile drug courts, and currently operates six such courts, which serve seven counties. The program provides comprehensive community-based services to juvenile offenders and their families (post-plea, but pre-final disposition). It runs approximately 50 weeks and is in four phases, each with distinct treatment goals and specified completion times. Participants are required to attend drug treatment, weekly court appearances, and meetings with a drug treatment court manager. To advance to the next phase, participants must have a specified number of weeks of clean alcohol and drug tests and no unexcused absences from treatment or court appearances. In addition to treatment for substance abuse, the program offers a variety of other services, such as educational programming, job training, mental health services, and recreational planning. The program functions through a collaboration between the Maine District Court, the Maine Department of Behavioral and Developmental Services/Office of Substance Abuse, and the Maine Department of Corrections/Juvenile Services.

Resource
Substance Abuse Treatment Initiative
Substance Abuse Treatment Initiative (S.A.T.I) is an evidence based, cutting edge Substance Abuse Treatment Program for Youth (12 - 18 years old), designed to provide area youth & their families an effective research-supported alternative
Resource
Juvenile Treatment Interventions
IDOC/DYS youth are given treatment interventions that include being placed in juvenile treatment programs, group therapy, and individual counseling/therapy. The number, intensity, and type of interventions for each youth is based upon their level of risk to reoffend and assessed criminogenic, mental health, educational, vocational, and aftercare needs.
Core treatment interventions
Treatment education programs, therapy groups, and mapping-enhanced counseling interventions teach youth pro-social skills, coping techniques, and strengths training to help them decrease their risk, address needs, increase resiliency, and improve their motivation and ability to re-enter their communities as positive, productive, and law-abiding citizens.
Treatment education programs include:
The Why Try Learning Strategies Program: Why Try is DYS’s core treatment education program. Why Try is brief, solution-focused treatment with a strengths-based approach to helping youth overcome their challenges, achieve positive goals, practice life skills, and develop plans and support for re-entering their community. Why Try teaches its treatment principles by pairing discrete cognitive-behavioral lessons with easy-to-remember pictures. These visual analogies (extended metaphors) teach social, coping, and emotional regulation skills to youth in a way they can understand and remember. Youth learn positive ways to answer the question “Why try in life?” through the visuals that include: The Motivation Formula; The Reality Ride; Tearing Off Labels; Defense Mechanisms; Climbing Out of the Pot; Jumping Hurdles; Desire, Time, and Effort; Lifting the Weight; and Getting Plugged In. The visual components of the Why Try Program are reinforced by supplements from a “Game Plan” Journal that includes short reflection writing; music and music-based projects; art projects; and hands-on, physical, and experiential activities. In this way, the program uses flexible lesson-planning with a variety of learning styles to teach the principles, reinforce the lessons, and maintain youth interest and engagement. To complete the program successfully, youth must successfully demonstrate mastery of the concepts and associated skills of Why Try as well as the ability to match them to individual risks, needs, strengths, and goals.
Effective Substance Abuse Prevention Programs
The Stay SHARP* Substance Abuse Education Program: The Stay SHARP* Program is DYS’s core juvenile substance abuse education program, and its name is also its organizing principle:
- S* = Seeking Motivation – Youth discuss: their use of alcohol and drugs, attempts to quit, and their level of motivation to explore their past, change their present, and examine their future.
- H* = How I Got Here (HIGH) – Youth read others’ stories of addiction and others’ reasons for getting high. They look deeper into their own stories and discover their own reasons for getting high.
- A* = Abuse or Addiction? – Youth learn the facts and destroy the myths behind abuse or addiction. They look at the general process or “stages” of abuse and addiction and examine their own individual stages. Youth learn how the benefits lessen and the consequences increase as they move down through the stages. Youth also receive detailed drug education about alcohol and substance use, abuse, chemical dependency, and addiction.
- R* = Ready for Change? – Youth learn that motivation is to the key to staying clean and sober. Like the “Reality Ride,” staying clean and sober is the much more difficult path and takes much more work than getting high, but it is worth it. Youth will examine reasons why it is worth it: why they should not go back to their old stage of abuse or addiction, why they and their lives are worth it, and what strengths they have that can help them.
- P* = Planning for the Future – Youth learn that they must plan ahead to minimize their risk to get high again and to maximize their level of motivation to succeed upon re-entry. Youth create a comprehensive Relapse Prevention / Re-Entry Plan to demonstrate that they have the knowledge and skills to follow through on these plans.
Individual/group therapyand mapping-enhanced counseling interventions are facilitated by trained mental health professionals. They include:
Treatment Readiness and Induction Program: TRIP is designed for delivery with youth who are in the recruit phase or orientation/induction phase of treatment. TRIP is facilitated by mental health professionals. The goal of TRIP is to help engage youth in the treatment process, to improve life skills and decision making, and to strengthen their commitment to remaining in treatment in order to fully address their treatment goals. TRIP is mapping-enhanced, motivation/engagement counseling created by Texas Christian University in partnership with DYS. TRIP also assists mental health staff in identifying which areas of Why Try can most help youth; which youth will require substance abuse therapy; and which youth need other treatment programs that will help them target their needs.
Advanced Relapse Prevention: ARP is group therapy for substance abuse/addiction recovery and is facilitated by mental health professionals. ARP targets youth with identified Moderate to High Substance Abuse / Addiction Recovery needs. These youth also attend the substance abuse education program component facilitated by DYS. ARP is mapping-enhanced, motivation/engagement counseling with an addiction recovery focus created by Texas Christian University in partnership with DYS.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy: DBT is facilitated by mental health professionals for youth who are selected by the treatment and mental health departments to participate because they:
- Experience ongoing difficulty dealing with stress management, pressure situations, and certain difficult people, places, and situations;
- Struggle dealing with chronic issues of frustration tolerance, anger management, impulsivity, acting out, and other behavior problems; and/or,
- Routinely need mental health contact, more intensive mental health interventions, and crisis interventions at times in order to function in their environment (facility and community).
DBT’s main focus will be to teach youth additional defense mechanisms from a menu of dialectical behavior therapy skills/techniques. DBT skills include mindfulness, emotion regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness skills.
Moral Reconation Therapy: MRT is a systematic treatment strategy that seeks to decrease recidivism among juveniles by increasing moral reasoning. MRT targets youth who are high risk to re-offend and/or are high risk in pro-criminal sentiments, criminal thinking, criminal lifestyle, and anti-social attitudes/values. MRT’s cognitive-behavioral approach combines elements from a variety of psychological traditions to progressively address ego, social, moral, and positive behavioral growth. MRT takes the form of group and individual counseling under the supervision of MRT-trained mental health professionals. MRT is structured around 16 objectively defined steps (units) focusing on seven basic treatment issues: confrontation of beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors; assessment of current relationships; reinforcement of positive behavior and habits; positive identity formation; enhancement of self-concept; decrease in hedonism and development of frustration tolerance; and development of higher stages of moral reasoning.
Other Targeted Need Interventions
These educational treatment programs with individual interventions are facilitated by DYS staff and target particular needs and areas of concern that impact youth success:
Anger Replacement Therapy: ART is a cognitive behavior, multi-modal curriculum comprised of three components: Structured Learning Training, Anger Control Training and Moral Reasoning. This program provides the youths with the means to lean self-control when their anger is aroused. Each step teaches the youth to reduce their anger and substitute pro-social behaviors. The anger cycle is taught in steps beginning with Triggers, Cues, Anger Reducers, Reminders and Self Evaluation.
Cage Your Rage: This program is designed to help juveniles understand and deal with anger by recording their feelings and actions. It will teach juveniles ways to not only recognize their anger but also control it through making appropriate choices. Chapters discuss; what causes anger, growing up with anger, how emotions develop, relaxation, managing anger, self talk, action controls, etc.
Cage Your Rage for Women: Cage Your Rage for Women is an anger management workbook specifically targeted to women. The exercises are intended for women working with their counselors either individually or in a group setting. Nevertheless, the workbook’s focus on women’s anger issues suggests that its content can be helpful to all women, not just those in counseling with a trained professional.
Growing Great Girls: This program is a gender responsive life skills curriculum. It focuses on decision-making skills, social resiliency, critical thinking skills, emotional knowledge, self-discovery and practical skills across six domains — physical, sexual, emotional relational, intellectual and spiritual. Designed for meaningful exchanges with small groups of girls, Growing Great Girlscreatively blends research-based interactive exercises with fun and meaningful worksheets.
Life Skills / Healthy Living: All facilities assist youth with developing skills to live as independent adults, such as grooming/hygiene, communication, relationship building, professional appearance, financial planning, and employability both in obtaining and maintaining employment.
Voices: Voices is a female specific program of self discovery and empowerment. It encourages girls to seek and celebrate their “true selves” by giving them a safe space, encouragement, structure, and support to embrace their important journey of self discovery. The focus is on issues that are important in the lives of adolescent girls from modules about self and connection with others to exploring health living and the journey ahead. The curriculum uses a variety of therapeutic approaches, including psycho-educational, cognitive-behavioral, expressive arts, and relational theory. It is based upon the Interactive Journaling system from Change Companies.
Specialty Units
DYS also delivers certain interventions and programs on specialty units that help youth and staff members create a treatment community and focus on more intensive treatment interventions:
Camp Summit: The entire facility is a specialty unit in that Camp Summit is Indiana’s only paramilitary and therapeutic boot camp that carefully blends military components with a programs approach to address the needs of adolescents and to afford the best possible environment for change and growth. Through the paramilitary, normative culture as well as full criminognenic and mental health programming/services, Camp Summit instills discipline, self-confidence, and individual responsibility in youth so that when they re-enter their communities they will have the opportunity to be productive citizens.
Clean Lifestyle Is Freedom Forever: CLIFF is a Logansport JCF therapeutic community unit. CLIFF is designed to provide services to youth who have experienced significant negative life experiences as a result of substance abuse or residing with family members who use substance abuse. The youth will receive individual counseling, group counseling, pro-social skills (life skills) and family counseling provided by Substance Abuse Counselors. Youth live together in a separate therapeutic community unit. Therapeutic Communities differ from other treatment approaches in such that they utilize the “community” as a methodology. Therapeutic members interact in a structured and unstructured environment that influences attitudes, perceptions, and behaviors associated with drug use. The youth are educated about addiction issues that have occurred or maybe occurring within their family unit. The focus of all treatment services is to provide youth with the tools necessary to change their thinking and behavior resulting in opportunities to develop and maintain a clean and sober lifestyle.
Future Solider Program: The purpose of this Pendleton JCF program is to identify youth who meet military enlistment criteria, develop and prepare them as legitimate military recruits, and arrange for their re-entry placement into one of the military branches whenever possible. The youth selected for this unit will have volunteered for the program, submitted an application, have reached the age of sixteen, and completed a formal interview process. Participation in this program in no way assures acceptance into the military; however, the facility will assist in the process. Program objectives are for youth to develop: a basic knowledge of military skills, good citizenship, self-reliance, leadership, responsiveness to constituted authority, the ability to communicate well, an appreciation for physical fitness, and an increase respect for the role of the US Armed Forces in support of national objectives.
Gang Realities in Our World: GROW is a Pendleton JCF program that focuses on gang intervention and personal growth. This program was inspired by the book “Gangbusters” written by Lonnie Jackson. Youth placed in this program are housed together in the same unit and attend gang intervention groups to work on developing appropriate pro-social bonds, understanding appropriate role models, victim empathy, etc.
Making a Change: Each DYS facility has a dedicated MAC group, MAC school, or full MAC Unit. They are for youth who are struggling with problematic behaviors that impact their ability to function well and consistently with other youth in general population. MAC programming refocuses youth through education, treatment, and mental health services while still maintaining a safe environment. The goal of this programming is to return all youth into general population settings as quickly as possible. Each facility has selected treatment staff and mental health professionals who develop an individual treatment plan with youth; provide individual counseling; facilitate groups that target problematic behaviors; provide frustration tolerance, impulse control, criminal thinking, and conflict resolution skills; and have benchmarks of progress to help the youth return to general population at the earliest opportunity after showing consistent improvement.
Community Substance Abuse Prevention Programs
Purposeful Living Units Serve: PLUS is offered at Logansport and Pendleton JCF. Youth live on a unit together and participate in a program that provides an opportunity for youth to explore and choose alternatives to criminal thinking and behavior through an emphasis on spiritual, moral, and character development. Youth also participate in life-skills training, community service projects, and intentional preparation for living as law abiding citizens who contribute to the well-being of their community.
Sex Offender Treatment and Education Program: STEP is a Pendleton JCF program that is provided to all youth who are adjudicated of a sex offense. Youth will be housed in a complex / single unit for the duration of their STEP programming but would be eligible for alternative housing once they have completed their individual STEP programming. The STEP Program is facilitated by Liberty counseling staff.
Venture Scouts Program: The purpose of this Pendleton JCF unit is to identify youth who are interested in developing their character, life skills, and commitment to the community through the principles of the BSA Venture Scouts Program. Unit counseling staff members are trained as BSA Venture Scout Leaders. The program's purpose is to provide positive experiences to help young people mature and to prepare them to become responsible and caring adults. Because they live on a unit together, the youth have a chance to learn and grow in a supportive and caring environment.
Youth Transition/Reintegration/Independent Living Unit: YTRI is a Logansport JCF privilege unit and less structured environment where the youth take responsibility for the basic operations and needs of the unit. It is set up like a college dormitory and allows for more freedom of movement within the unit. These youth are role models, assist in mentoring new youth, and take part in a program based on “The 40 Developmental Assets.” YTRI youth also learn—experientially—about how to develop higher moral standards and mature character through intentional acts of kindness and service to others. All of this is geared to give them positive experiences and expectations of being productive citizens in a community. Youth are then assisted in planning how to translate these skills to their transition / reintegration into their home community.
Community Volunteer Treatment Programs
Every facility has a wide array of community-sponsored and volunteer groups that provide structured activities, religious services, tutoring services, and mentoring that keep youth busy and productive. These programs also help youth have fun, earn privileges, receive rewards, and develop positive relationships with community members, other youths, and adult role models. However, some of these groups also include interventions that address targeted treatment issues with youth, including:
AA/NA:Each facility has community volunteers that provide AA/NA support meetings, counseling, and a framework for self-examination and a road to recovery.
Bienvenido: This program, offered at all facilities, is a strengths-based mental health promotion program that provides youth an opportunity to vent their experiences regarding incarceration; establish a relationship with a community leader; and learn how to create ways to improve mental health and self-esteem while in a facility. The program also assists adolescents in becoming more involved in their school and community. The program covers such topics as positive thinking, time-management, stress-management, suicide prevention, self-discipline and fitting in. Art, dance, yoga and conflict resolution training are some things that have been used to stimulate discussion with the youth.
Hope and Loss: This is a Madison JCF program, facilitated by the chaplain, to address the concerns and pain of youth who have experienced painful loss. The group allows youth to define their own personal losses and encourages them to face the loss, identify their
Center For Substance Abuse Prevention
Partners in Health: These trained community providers lead programs at all facilities but tailored to each facility’s population in the areas of sex education, healthy relationships, and parenting.
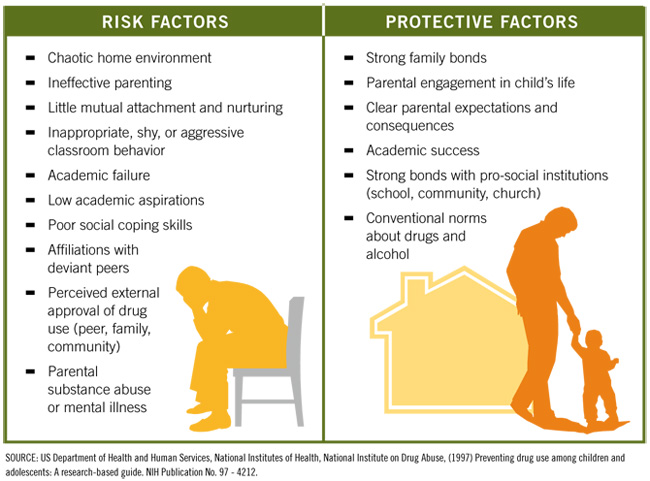
Peace Learning: In partnership with the Indiana Department of Correction and Federal Title 1 and Federal Title II, Peace Learning Center implements an intensive peace education program at Pendleton JCF that blends conflict resolution and diversity skills with challenge education that promotes personal responsibility for success. Youth learn non-violent coping mechanisms in a way that incorporates mind, body, nature and self-discovery. The Peace Learning Program is a holistic approach to positive change. Peace Learning Center’s programs focus on building these protective factors in youth.